LCFS developments: proposal to simplify application process
July 2, 2014
BY John Sens
On May 31, the California Air Resources Board held a workshop outlining some of its proposed changes to the low carbon fuel standard (LCFS) program. Among the changes proposed were those related to the new pathway submission and evaluation process.
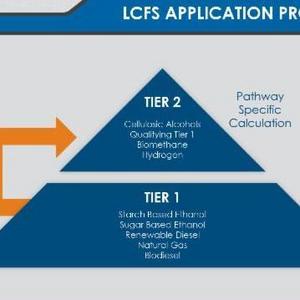
CARB outlined a proposal to group all biofuels into a two-tier system. Tier 1 fuels are conventionally produced fuels, including sugar and starch based ethanol, biodiesel, renewable diesel, and natural gas produced through conventional means. Tier 2 fuels include advanced fuels such as cellulosic alcohols, biomethane, and hydrogen. A Tier 1 fuel could become a Tier 2 fuel if the facility utilizes specific innovative methods such as carbon capture and sequestration, use of renewable energy sources, reduced emissions from feedstock production, and any other innovations to increase efficiency and reduce CO2 (or equivalent) output.
Under the proposed system, CARB will provide a simplified GREET model calculator for Tier 1 fuels, and producers will be able to enter operational data at the plant such as energy consumption, yield ratios and coproduct volumes. The calculator will then provide the carbon intensity (CI) value for the facility. This will save applicants’ time and resources currently spent on creating custom GREET models for their facility and staff time currently spent on reviewing new custom GREET models and pathway applications.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Tier 1 fuel producers who have submitted new pathways, which were approved in the current system, will be grandfathered into the new system and can utilize their approved pathways to generate CI credits. They can also elect to reapply in the new system (using the GREET model calculator).
Tier 2 fuels will require a method 1 or 2 application just like they do now. They will either utilize an established Lookup Table value (Method 1), or use an existing pathway as a reference (Method 2A), or create a brand new pathway to be utilized (Method 2B). Producers wishing to use the Method 2A application process will need to meet substantiality requirements, which are dependent on the CI value for their fuel relative to the reference pathway. The requirements are proportional: the new pathway must be 5.5 percent below the reference for pathways over a CI of 20gCO2e/MJ, or 1gCO2e/MJ below pathways under a CI of 20.
CARB is still working out the finer details of the new process and is seeking comments to make the system as strong as possible. Proposed changes and notes from the workshops are available at the LCFS website. To submit comments, you can contact the LCFS staff.
Author: John Sens
Advertisement
Advertisement
Compliance Specialist, EcoEngineers
515-419-4783
jsens@ecoengineers.us
Related Stories
International Sustainability & Carbon Certification has announced that Environment and Climate Change Canada has approved ISCC as a certification scheme in line with its sustainability criteria under its Clean Fuel Regulations.
Legislation introduced in the California Senate on June 23 aims to cap the price of Low Carbon Fuel Standard credits as part of a larger effort to overhaul the state’s fuel regulations and mitigate rising gas prices.
The government of Brazil on June 25 announced it will increase the mandatory blend of ethanol in gasoline from 27% to 30% and the mandatory blend of biodiesel in diesel from 14% to 15%, effective Aug. 1.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit on June 20 rejected several claims challenging the U.S. EPA’s RFS Set rule but will require the agency to provide additional information on certain environmental findings.
The 2025 International Fuel Ethanol Workshop & Expo, held in Omaha, Nebraska, concluded with record-breaking participation and industry engagement, reinforcing its role as the largest and most influential gathering in the global ethanol sector.
Upcoming Events










