ePURE: EU ethanol hits new record for GHG reduction


SOURCE: ePURE
June 16, 2023
BY ePURE
Production and use of renewable ethanol from ePURE members reduced greenhouse-gas emissions by an average of 78.4 percent compared to fossil fuels in 2022, according to newly certified data. It was the 11th consecutive year in which EU renewable ethanol increased its GHG-reduction score.
The record-breaking figure highlights the continuing innovation of the European renewable ethanol industry as biorefineries decrease emissions and improve the already impressive sustainability of EU crop-based and advanced biofuels.
The new data comes as policymakers determine what role sustainable biofuels such as renewable ethanol can play in the drive to carbon-neutrality.
Advertisement
Advertisement
“Domestic production of EU renewable ethanol has never been more strategically important, contributing to Europe’s food security, energy independence and and transport decarbonization goals,” said David Carpintero, director general of ePURE, the European renewable ethanol association.
“Every year ePURE members improve their production processes with solutions that aren’t just on the drawing board but already deliver results now – including capture of biogenic CO2 and increased production of food, feed and fuel,” Carpintero added. “This places Europe’s renewable ethanol industry as a world leader in terms of sustainability.”
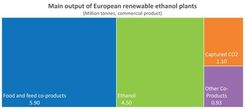
The record-high GHG-saving performance of ePURE members’ ethanol was also accompanied by significant production of food and feed co-products (5.9 million metric tons of commercial product) and of captured CO2 (1.1 million metric tons) – more ways in which ethanol production contributes to EU food security and offsets fossil fuel use.
Once again, ePURE members produced more food and feed co-products than renewable ethanol – more food than fuel.
Advertisement
Advertisement
The 2022 findings were compiled from ePURE members and certified by auditing firm Copartner.
ePURE’s membership includes 21 producing companies with around 50 refineries across the EU and UK, accounting for about 85 percent of EU renewable ethanol production.
Related Stories
U.S. fuel ethanol capacity fell slightly in April, while biodiesel and renewable diesel capacity held steady, according to data released by the U.S. EIA on June 30. Feedstock consumption was down when compared to the previous month.
XCF Global Inc. on July 8 provided a production update on its flagship New Rise Reno facility, underscoring that the plant has successfully produced SAF, renewable diesel, and renewable naphtha during its initial ramp-up.
The USDA’s Risk Management Agency is implementing multiple changes to the Camelina pilot insurance program for the 2026 and succeeding crop years. The changes will expand coverage options and provide greater flexibility for producers.
EcoCeres Inc. has signed a multi-year agreement to supply British Airways with sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). The fuel will be produced from 100% waste-based biomass feedstock, such as used cooking oil (UCO).
SAF Magazine and the Commercial Aviation Alternative Fuels Initiative announced the preliminary agenda for the North American SAF Conference and Expo, being held Sept. 22-24 at the Minneapolis Convention Center in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
Upcoming Events










