China's fuel ethanol consumption expected to fall in 2022
September 20, 2022
BY Erin Krueger
A report filed with the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service’s Global Agricultural Information Network indicates that China’s ethanol blend rate is expected to reach only 1.8 percent this year as support wanes for previously announced biofuel policies.
China had planned to implement a nationwide E10 mandate by 2020. While E10 remains the official policy, the report notes that actual blend rates vary and are often significantly lower, even in locations with an E10 program. The GAIN report discusses rumors that China may unofficially move to an E5 mandate in the coming years, but notes the government insists E10 remains in force.
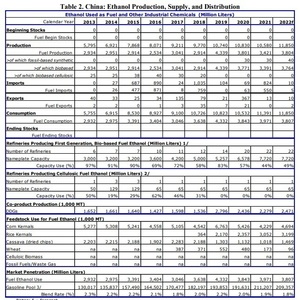
China is expected to consume 11.85 billion liters (3.13 billion gallons) of ethanol this year, including 3.807 billion liters of fuel ethanol. Total ethanol consumption was at 11.391 billion liters in 2021 and 10.532 billion liters in 2020, with fuel ethanol consumption at 3.971 billion liters last year and 3.843 billion liters in 2020. If China had fully implemented a national E10 blending program by 2020, the report estimates the country would have consumed approximately 19 billion liters of fuel ethanol that year, roughly five times greater than actual consumption.
Advertisement
The fuel ethanol blend rate is expected to average 1.8 percent this year, down from 1.9 percent last year and 2 percent in 2020.
China currently has 22 fuel ethanol refineries, flat with 2021, but up from 20 in 2020. Nameplate capacity for 2021 and 2022 is estimated at 7.72 billion liters, up from 6.578 billion liters in 2020. Capacity utilization is expected to reach 49 percent this year, up from 44 percent in 2021, but down from 57 percent in 2020.
Total domestic ethanol production is expected to reach 11.85 billion liters in 2022, up from 10.58 billion liters in 2021 and 10.83 billion liters in 2020. Fuel ethanol production is expected to reach 3.804 billion liters this year, up from 3.391 billion liters in 2021, but down from 3.771 billion liters in 2020. Approximately 40 million liters of domestic fuel ethanol production this year is expected to be fossil-based synthetic ethanol, compared to 30 million liters in 2021 and 2020.
Advertisement
Corn is expected to be the primary feedstock for fuel ethanol production in China this year, with 4.694 million metric tons expected to be consumed. Fuel ethanol producers in China are also expected to consume 3.199 million metric tons rice, 1.469 million metric tons of cassava and 96,000 metric tons of wheat as feedstock this year.
China is expected to import 10 million liters of ethanol this year, including 5 million liters of fuel ethanol. Imports were at 824 million liters last year, including 550 million liters of fuel ethanol, and 69 million liters in 2020, including 63 million liters of fuel ethanol. Ethanol exports are expected to reach 10 million liters in 2022, including 2 million liters of fuel ethanol. Total ethanol exports were at 13 million liters in 2021 with no fuel ethanol exports and at 367 million liters in 2020, including 21 million liters of fuel ethanol.
A full copy of the report can be downloaded from the USDA FAS GAIN website.
Related Stories
The U.S. EPA on July 8 hosted virtual public hearing to gather input on the agency’s recently released proposed rule to set 2026 and 2027 RFS RVOs. Members of the biofuel industry were among those to offer testimony during the event.
The U.S. exported 31,160.5 metric tons of biodiesel and biodiesel blends of B30 and greater in May, according to data released by the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service on July 3. Biodiesel imports were 2,226.2 metric tons for the month.
The USDA’s Risk Management Agency is implementing multiple changes to the Camelina pilot insurance program for the 2026 and succeeding crop years. The changes will expand coverage options and provide greater flexibility for producers.
EcoCeres Inc. has signed a multi-year agreement to supply British Airways with sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). The fuel will be produced from 100% waste-based biomass feedstock, such as used cooking oil (UCO).
CARB on June 27 announced amendments to the state’s LCFS regulations will take effect beginning on July 1. The amended regulations were approved by the agency in November 2024, but implementation was delayed due to regulatory clarity issues.
Upcoming Events










