Dyadic unveils new enzyme for biofuel and biochemical production



July 16, 2012
BY Dyadic International Inc.
Dyadic International Inc. a global biotechnology company focused on the discovery, development, manufacture and sale of enzymes and others proteins for the bioenergy, bio-based chemical, biopharmaceutical and industrial enzyme industries, today unveiled its latest biofuels enzyme advancement, AlternaFuel CMAX3. This next generation product enables the production of cellulosic biofuels and bio-based chemicals from a wide range of renewable non-food feedstocks under broad operating conditions.
“The data supporting this product clearly demonstrates Dyadic’s scientific capabilities to leverage our C1 technology platform to create enzyme mixtures whose performance rivals the leading biofuels enzyme product on the market,” said Mark Emalfarb, Dyadic’s president and CEO. “This is largely due to the inherent robustness and versatility of the C1 genome and expression system, both of which have considerable untapped potential. The results obtained with AlternaFuel CMAX3 are not only relevant for the production of biofuels but also for bio-based chemicals and biogas. Dyadic and its licensees are continuing to develop better performing enzymes to further reduce the total cost of producing advanced biofuels and other bio-based products.”
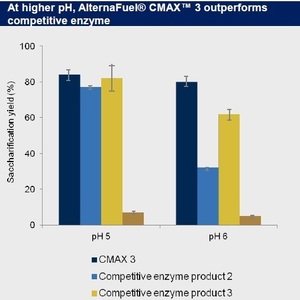
“AlternaFuel CMAX3 achieved a similar saccharification yield at pH 5.0 and substantially better results at pH 6.0 than those achieved by the current leading competitive biofuels enzyme product,” said Jan Wery, science director at Dyadic Netherlands. “Saccharification yield is defined as the relative amount of fermentable sugars released through enzymatic hydrolysis from lignocellulosic biomass such as agricultural feedstock and waste. This important parameter demonstrates the level of progress being made across the entire industrial enzyme industry in developing enzymes necessary for lignocellulosic biomass to replace petroleum in fuel and chemical production.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Related Stories
The U.S. Department of Energy Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) announced up to $23 million in funding to support research and development (R&D) of domestic chemicals and fuels from biomass and waste resources.
The U.S. DOE has announced its intent to issue funding to support high-impact research and development (R&D) projects in two priority areas: sustainable propane and renewable chemicals and algal system cultivation and preprocessing.
Sens. Sherrod Brown, D-Ohio, and Pete Ricketts, R-Neb., in August introduced the Renewable Chemicals Act, a bill that aims to create a tax credit to support the production of biobased chemicals.
The Chemical Catalysis for Bioenergy Consortium, a consortium of the U.S. DOE’s Bioenergy Technologies Office, has launched an effort that aims to gather community input on the development of new biomass processing facilities.
USDA on March 8 celebrated the second annual National Biobased Products Day, a celebration to raise public awareness of biobased products, their benefits and their contributions to the U.S. economy and rural communities.
Upcoming Events










