EIA: Subsidies for renewables down as tax credits diminish




U.S. Energy Information Administration
April 30, 2018
BY U.S. Energy Information Administration
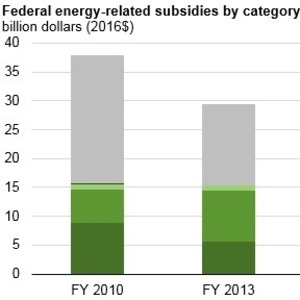
Federal subsidies for renewable energy—including biofuels for transportation use and renewable generation of electricity—dropped to $6.7 billion in fiscal year (FY) 2016, a 56 percent decline from FY 2013. Renewable subsidies in FY 2010 and FY 2013 were approximately $15 billion, more than double FY 2016 levels, as support from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 lessened. Despite the decline, renewable energy continued to receive a large share of total federal energy subsidies, accounting for 46 percent of the FY 2016 total.
EIA's updated report continues a data series that began at the request of Congress in the early 1990s. Most recently, the Secretary of Energy requested updated energy subsidy information as part of the U.S. Department of Energy’s study on grid resiliency.
EIA’s recently released Direct Federal Financial Interventions and Subsidies in Energy in Fiscal Year 2016 report provides a detailed analysis of energy subsidies for FY 2010, FY 2013, and FY 2016. This report examines only federal subsidies and financial interventions that are targeted exclusively at energy markets and have an identifiable budget impact.
Advertisement
In the report, EIA defines subsidies as funds a government expends, or revenue it foregoes, to encourage or support certain activities. EIA’s report includes the following financial activities: direct expenditures, tax expenditures, research and development (R&D), and credit subsidies to recipients of federal loan guarantees.
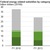
Tax expenditures provided 80 percent of FY 2016 renewables subsidies. More than half (51 percent) of the $5.6 billion in renewable tax expenditures went to biofuels. Biofuels accounted for 77 percent of tax expenditures in FY 2010, but only 31 percent in FY 2013, largely because of the expiration of the Volumetric Ethanol Excise Tax Credit at the end of 2011. Biofuels tax expenditures increased nearly $1 billion between FY 2013 and FY 2016 (from $1.7 billion to $2.7 billion) as a result of the $1 per gallon biodiesel blenders tax credit. The Renewable Fuel Standard, which mandates the blending of biofuels into the nation’s fuel supply, generated demand for these fuels by increasing targets.
Renewable electricity-related tax expenditures provided nearly 70 percent of FY 2013 renewable electricity subsidies, falling to about half that share in FY 2016. Most of this amount went to commercial wind and solar installations from the Production Tax Credit and the Investment Tax Credit. The PTC provided an inflation-adjusted tax credit worth 2.4 cents per kilowatthour (kWh) in 2016, while the ITC provided a deduction equal to 30 percent of facility installation costs. EIA estimates the PTC and ITC credits taken in FY 2016 at $1.4 billion and $1.2 billion, respectively.
Advertisement
Nearly all renewable energy direct expenditures for FY 2010, FY 2013, and FY 2016 resulted from provisions of ARRA. Enacted in 2009, ARRA was a broad-based set of programs designed to expedite economic recovery, including energy infrastructure. Under ARRA, DOE has invested more than $31 billion since 2009. Much of this funding supported renewable energy projects, but by FY 2016, most provisions of ARRA energy programs had expired. Direct expenditures for renewable energy decreased 90 percent, from nearly $9 billion in FY 2013 to about $1 billion in FY 2016.
Although R&D expenditures are small compared with tax expenditures and direct expenditures, R&D provides the foundation for many energy technology advancements and cost reductions. Federal R&D expenditures for renewable energy were estimated at about $850 million for FY 2010 and FY 2013, but they dropped to about $450 million in FY 2016. Another $296 million in federal loan guarantees was distributed to recipients in FY 2010, but in both FY 2013 and FY 2016, federal loan guarantee subsidies were zero.
Related Stories
The U.S. Department of Energy Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) announced up to $23 million in funding to support research and development (R&D) of domestic chemicals and fuels from biomass and waste resources.
The U.S. DOE has announced its intent to issue funding to support high-impact research and development (R&D) projects in two priority areas: sustainable propane and renewable chemicals and algal system cultivation and preprocessing.
Sens. Sherrod Brown, D-Ohio, and Pete Ricketts, R-Neb., in August introduced the Renewable Chemicals Act, a bill that aims to create a tax credit to support the production of biobased chemicals.
The Chemical Catalysis for Bioenergy Consortium, a consortium of the U.S. DOE’s Bioenergy Technologies Office, has launched an effort that aims to gather community input on the development of new biomass processing facilities.
USDA on March 8 celebrated the second annual National Biobased Products Day, a celebration to raise public awareness of biobased products, their benefits and their contributions to the U.S. economy and rural communities.
Upcoming Events










