Latest diesel quality trends revealed in biennial survey

April 26, 2016
BY Infineum International Ltd.
Infineum has revealed the initial results from its latest biennial global Winter Diesel Fuel Quality Survey, offering a unique update on the current trends in the industry across the global marketplace.
The Infineum survey collected samples from service stations from across eight countries in order to represent the production from each refinery or region in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, New Zealand, Peru and South Africa. The latest findings cover the results of the Southern Hemisphere, with the full results set to be announced in October.
The data from this year’s samples offers further insight into some of the diesel industry’s most prominent topics, including the use of renewable fuels, the decrease in fuel sulfur levels, and the trends in oxidation and cloud point.
Monitoring the rise of FAME
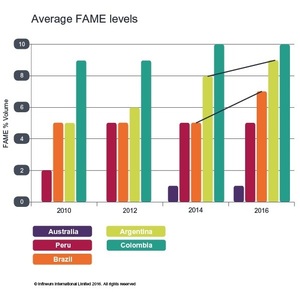
This year’s report shows a continuing state of flux for the presence of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) in samples throughout the Southern Hemisphere, aligned with varying uses of biodiesel in each of the nations surveyed. FAME is well known as an effective method of improving lubricity, but the associated costs can be prohibitive in their application.
In Australasia, only New South Wales currently mandates the use of FAME for biodiesel, with the level currently set at 2 percent. This year’s Winter Diesel Fuel Quality Survey reported evidence of a sample which contained 4 percent—the same level recorded in Infineum’s 2012 survey.
No FAME samples were found in New Zealand, although this may change in future surveys as Z Energy’s 20 MMly biodiesel plant comes online. The company says its B5 drop-in biodiesel blend will be available in certain regions towards the middle of 2016, even though biodiesel is neither mandatory nor subsidized in New Zealand.
Meanwhile, levels of FAME in Latin America ranged from 0 percent in Chile to 11 percent in Argentina. This result is to be expected due to the considerable variation in the mandates of FAME use across this diverse region.
In Brazil, the government set a 7 percent blending ratio in 2014 and the biodiesel industry is advocating a B10 blend by 2020 as the industrial capacity is more than twice the actual production target and raw material is available. Argentina and Colombia already boast 10 percent biodiesel blending ratios while Peru currently mandates B5. Chile is the only country sampled in the region with no mandated blending levels in place.
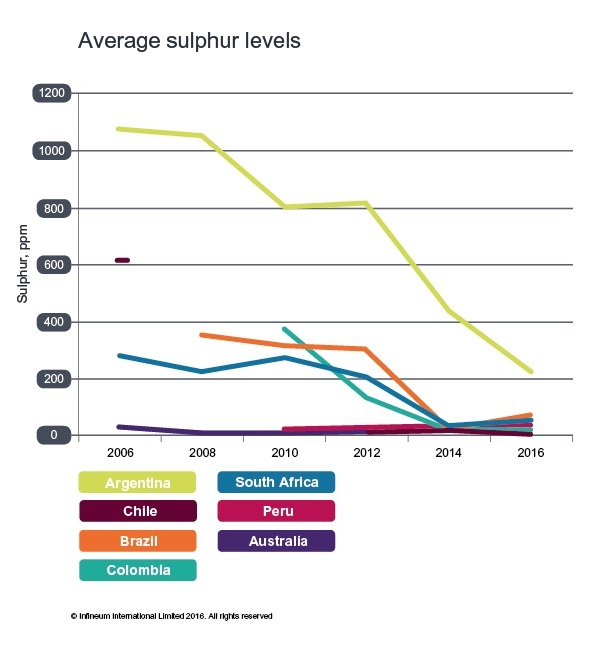
Downward sulfur levels trend continues
Sulfur levels have continued to fall over the past two years, following a significant decline in levels between 2012 and 2014, with average figures in some countries falling from hundreds to just tens of ppm.
Advertisement
Advertisement
However, this year’s survey shows one sample from Brazil and one from South Africa with high sulfur levels, meaning the average sulfur measured for these two countries has increased. This may be down to the influence of sample collection since rural diesel tends to have higher sulfur levels than city diesel.
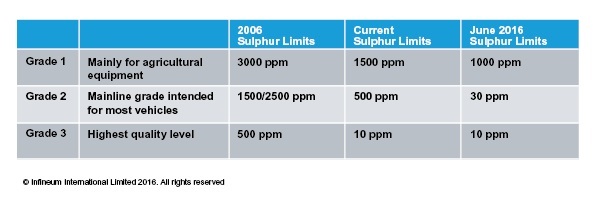
Argentina has offered perhaps the most notable results from this year’s survey. Average sulfur levels in the South American nation have fallen by 73 percent since 2012 and it is the only country sampled that has maintained an average sulfur level in the hundreds rather than tens of ppm. The country has achieved a 49 percent decrease in its average sulfur levels from 2014 alone.
Argentina has three grades of diesel and the sulfur limits have been tightened regularly since their introduction in 2006. We might expect the sulfur cuts scheduled in June 2016 to mean results from the Infineum 2018 survey will show an average figure more in line with other Latin American countries.
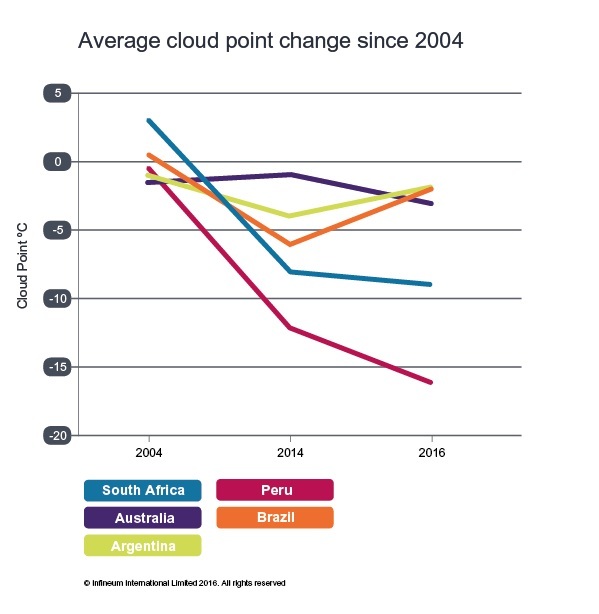
Counting the cloud point
Overall, the cloud point (CP) of the Southern Hemisphere samples appears to be lower in 2016 compared to 2004. Over the 2014-’16 period, South Africa and Peru have continued this trend, while the reverse has been seen in Argentina and Brazil.
The causes of this movement in cloud point are likely to include, but may not be limited to:
1. The need to reduce back-end distillation to facilitate sulfur reduction
2. Increased use of imported diesel in some locations
3. Specification changes
4. Sampling variation
Advertisement
Advertisement
5. Seasonal formulation differences
Regardless of the cause, refiners have managed to maintain consistent fuel quality with all fuels remaining on specification.
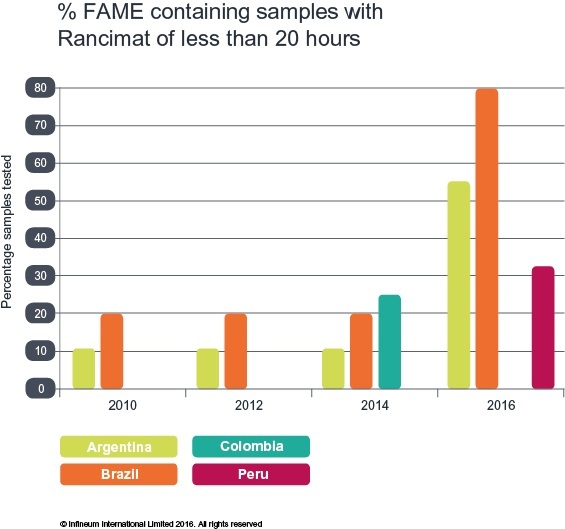
Oxidation stability worsening
This year’s survey records a significant worsening in oxidation stability in the samples from Argentina and Brazil, while a reasonable percentage of samples from Peru were also found to have a Rancimat of less than 20 hours.
The cause of this trend is unclear, although it could be attributed to poor FAME quality or a lack of antioxidant additive use. In certain circumstances poor oxidation stability can lead to higher levels of particulate matter in fuels, which has the potential to cause filterability issues and may result in fuel starvation and engine operating difficulties.
While it is not possible to attribute a cause, on examination of the filterability results, two samples from Argentina, both with Rancimat of less than 10 hours, failed to meet filterability targets.
Byproducts of oxidation may be contributory factors in fuel filterability performance and in reducing vehicle filter longevity. However, several other factors need to be considered when analyzing field issues related to filter blocking.
Looking ahead—first look at European marine fuels
It is essential to closely monitor the quality of the wider portfolio of diesel fuels as the global demand for fuel continues to increase and products become more complex. Regularly assessing the changing landscape will ensure that diesel products meet the specific requirements for each market and application.
For the first time, the 2016 Winter Diesel Fuel Quality Survey will include data on the quality of marine bunker fuels sampled in European Emission Control Areas. The results will be made available in October this year.
To read the full Infineum Winter Diesel Fuel Quality Survey Southern Hemisphere results, click here.
Related Stories
Clean Fuels Alliance America on June 10 announced the launch of the newly redesigned BQ-9000 website, delivering a streamlined and user-friendly experience that better showcases the value of biodiesel quality assurance.
Global Biofuels Alliance launches at G20 Summit
President Joe Biden on Sept. 9 joined leaders of India, Argentina, Brazil, Italy, Mauritius and the United Arab Emirates to launch the Global Biofuels Alliance. The launch took place on the sidelines of the G20 Summit in New Delhi.
Neste is disputing a report filed with the USDA that suggests the company may have received fraudulent used cooking oil (UCO) volumes at its renewable products refinery in Singapore, specifically virgin palm oil from Indonesia.
Clean Fuels outlook predicts growing supplies of used cooking oil
Global used cooking oil (UCO) supplies are anticipated to rise from 3.7 billion gallons in 2022 to between 5 billion and 10 billion gallons by 2030, according to a report released by Clean Fuels Alliance America on Sept. 13.
Korean Air will launch a program to use SAF for air cargo operations in cooperation with air cargo customers and forwarders. Customers can make customized contributions through the program that Korean Air will use to purchase SAF.
Upcoming Events