Renewable share of US energy consumption highest since 1930s

Source: EIA
May 28, 2015
BY The U.S. Energy Information Administration
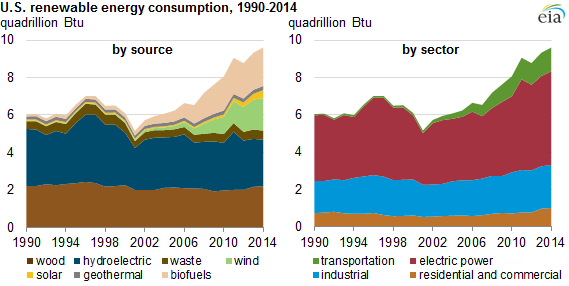
Renewable energy accounted for 9.8 percent of total domestic energy consumption in 2014. This marks the highest renewable energy share since the 1930s, when wood was a much larger contributor to domestic energy supply.
Renewable energy use grew an average of 5 percent per year over 2001-‘14 from its most recent low in 2001. The increase over the past 14 years was in part because of growing use of wind, solar, and biofuels. Wind energy grew from 70 trillion Btu in 2001 to more than 1,700 trillion Btu in 2014. During the same period, solar energy (solar thermal and photovoltaic) grew from 64 trillion Btu to 427 trillion Btu, and the use of biomass for the production of biofuels grew from 253 trillion Btu to 2,068 trillion Btu. Hydroelectricity was the largest source of renewable energy in 2014, but hydro consumption has decreased from higher levels in the mid-to-late 1990s. Wood remained the second-largest renewable energy source, with recent growth driven in part by demand for wood pellets.
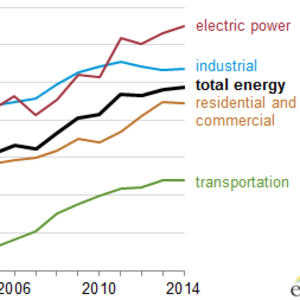
In 2014, slightly more than half of all renewable energy was used to generate electricity. Within the electric power sector, renewable energy accounted for 13 percent of energy consumed, higher than its consumption share in any other sector.
The industrial sector used 24 percent of the nation's renewable energy in 2014. Nearly all of that renewable energy was biomass, which included wood, waste, and biofuels used in manufacturing processes as well as in the production of heat and power. The production of biofuels results in energy losses and coproducts, which are also included in industrial consumption of renewables.
Advertisement
About 13 percent of the renewable energy used in the U.S. is now consumed in the transportation sector, which experienced the largest percentage growth in renewable consumption from 2001 to 2014. The growing demand for liquid biofuels, including both ethanol and biodiesel, pushed renewables to nearly 5 percent of the sector's energy consumption in 2014.
A greater use of wood for home heating and steadily growing installation of solar systems are the main contributors to increasing renewable energy consumption in residential buildings and, to a lesser extent, in commercial buildings.
Advertisement
Related Stories
ATOBA Energy and Air Moana are partnering to implement scalable solutions for the supply of SAF. The collaboration aims to ensure long-term SAF availability while supporting local initiatives to develop sustainable fuel production in Tahiti.
Kintetsu World Express Inc. has signed an additional agreement with Hong Kong, China-based Cathay Pacific Airways for the use of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). The agreement expands a three-year partnership between the two companies.
Broco Energy on July 17 announced a new partnership with the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport) to deliver and transition Massport's fuel tanks to renewable diesel across its various facilities.
Shell Aviation, Accenture, and Amex GBT on July 10 announced Avelia is in the process of evolving to an industry solution with independent data hosting and a multi-supplier model helping users access the GHG benefits of SAF.
Avia Solutions Group, the world's largest ACMI (aircraft, crew, maintenance, and insurance) provider, has partnered with DHL Express to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from its international shipments using SAF.
Upcoming Events










