Study successfully integrates sweet sorghum juice in corn mash
Sorghum Checkoff
May 9, 2013
BY Sorghum Checkoff
The Sorghum Checkoff in collaboration with the NCERC at Southern Illinois University Edwardsville (formerly the National Corn-to-Ethanol Research Center) is pleased to announce a successful bench-scale evaluation of sweet sorghum juice sugars with corn mash for the production of fuel ethanol. This study expands upon a commercial-scale trial that was conducted in Hopkinsville, Ky., in late 2012 by Commonwealth Agri-Energy LLC, Delta BioRenewables LLC, Ceres Inc. and the Sorghum Checkoff.
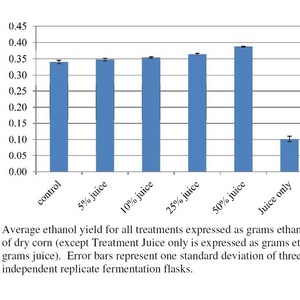
The bench-scale study yielded critical data on the production of ethanol from a combination of the two feedstocks by evaluating fermentation performance at different levels of sweet sorghum juice inclusion in corn mash. The sugar juice was successfully used as a replacement for process water, demonstrating the potential for a corn ethanol plant to increase production above nameplate capacity by incorporating sweet sorghum juice sugars.
Advertisement
Advertisement
“This analysis was extremely successful at the lab scale, and suggests that sweet sorghum juice inclusion could increase the throughput of existing corn ethanol facilities. In addition to increased yields, sorghum juice inclusion may reduce enzyme and nutrient usage per gallon of ethanol produced. Sweet sorghum juice sugar can also help ethanol producers diversify their feedstocks and serve as a bridge to the next generation of biofuels,” said Sabrina Trupia, NCERC assistant director of research.
John Duff, Sorghum Checkoff renewables program director, says the success of the trial is validation sweet sorghum juice sugars are fully compatible and maybe even synergistic with corn mash in ethanol production.
“Before a corn ethanol plant will take a step toward that next generation it must be confident in its ability to do so successfully,” Duff said. “We think this study will help provide that assurance and support the commercialization of sweet sorghum as a new industrial sugar feedstock crop across the broad geographic area of the country where it can be grown.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
The Sorghum Checkoff and NCERC recognize Delta BioRenewables and Commonwealth Agri-Energy for their input into the study’s experimental design. Delta BioRenewables provided the sweet sorghum juice used in the study.
For more information on details regarding the trial’s methodology and results, click here.
Related Stories
The USDA significantly increased its estimate for 2025-’26 soybean oil use in biofuel production in its latest World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates report, released July 11. The outlook for soybean production was revised down.
U.S. fuel ethanol capacity fell slightly in April, while biodiesel and renewable diesel capacity held steady, according to data released by the U.S. EIA on June 30. Feedstock consumption was down when compared to the previous month.
The U.S. EPA on July 8 hosted virtual public hearing to gather input on the agency’s recently released proposed rule to set 2026 and 2027 RFS RVOs. Members of the biofuel industry were among those to offer testimony during the event.
The USDA’s Risk Management Agency is implementing multiple changes to the Camelina pilot insurance program for the 2026 and succeeding crop years. The changes will expand coverage options and provide greater flexibility for producers.
The USDA’s National Agricultural Statistics Service on June 30 released its annual Acreage report, estimating that 83.4 million acres of soybeans have been planted in the U.S. this year, down 4% when compared to 2024.
Upcoming Events










