EPA: 15 new small refinery exemption petitions filed for 2018
SOURCE: U.S. EPA
February 21, 2019
BY Erin Krueger
On Feb. 21, the U.S. EPA released updated data on small refinery hardship waivers filed under the Renewable Fuel Standard, reporting that 15 new waivers for the 2018 compliance year were filed between Dec. 18, 2018 and Feb. 10, 2019.
Under the regulations that establish the Renewable Fuel Standard, small refineries may petition the EPA annually for an exemption from their RFS obligations. The agency can grant the exemption if it determines the small refinery has demonstrated disproportionate economic hardship, as described under the RFS regulations. When the EPA grants an exemption, the exempted refinery does not have to meet the RFS requirements for the compliance year for which the exemption was granted.
As of Feb. 10, the EPA has received 37 petitions seeming small refinery waivers for the 2018 compliance year, up from 22 petitions that had been filed as of Dec. 18 of last year. All 37 petitions are still pending.
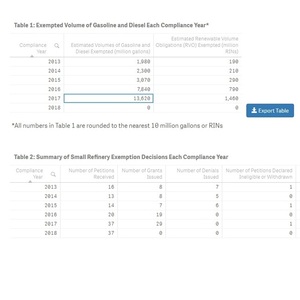
No new petitions were filed for approved for compliance years 2013 through 2017.
Advertisement
Advertisement
EPA data currently shows 37 small refinery petitions were filed for the 2017 compliance year. To date, the agency has approved 29 petitions, with seven currently pending and one declared ineligible or withdrawn. The 29 petitions approved to date have exempted approximately 1.46 billion renewable identification numbers (RINs), or approximately 13.62 billion gallons of gasoline and diesel from meeting the RFS blending targets.
For compliance year 2016, the EPA has received 20 small refinery petitions, with 19 approved to date and one still pending. The 19 approved petitions have exempted approximately 790 RINs, or 7.84 billion gallons of gasoline and diesel from meeting RFS blending targets.
For compliance year 2015, the EPA received 14 petitions. The agency approved seven petitions and denied eight. One petition was declared ineligible or withdrawn. The seven approved petitions have exempted approximately 290 million RINs, or 3.07 billion gallons of gasoline and diesel from meeting RFS blending targets.
The EPA received 13 small refinery petitions for compliance year 2014. The agency approved eight petitions, but denied the remaining five. The eight approved petitions exempted 210 million RINs, or approximately 2.3 billion gallons of gasoline and diesel from meeting RFS blending targets.
Advertisement
Advertisement
For the 2013 compliance year, EPA received 16 petitions. The agency approved eight and denied seven. One petition was declared ineligible or withdrawn. The eight approved petitions exempted 190 million RINs, or approximately 1.98 billion gallons of gasoline and diesel form meeting RFS blending obligations.
The EPA is expected to update data on small refinery hardship waivers monthly, with the next update expected to be released in mid-March.
Related Stories
The U.S. Energy Information Administration maintained its forecast for 2025 and 2026 biodiesel, renewable diesel and sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) production in its latest Short-Term Energy Outlook, released July 8.
XCF Global Inc. on July 10 shared its strategic plan to invest close to $1 billion in developing a network of SAF production facilities, expanding its U.S. footprint, and advancing its international growth strategy.
U.S. fuel ethanol capacity fell slightly in April, while biodiesel and renewable diesel capacity held steady, according to data released by the U.S. EIA on June 30. Feedstock consumption was down when compared to the previous month.
XCF Global Inc. on July 8 provided a production update on its flagship New Rise Reno facility, underscoring that the plant has successfully produced SAF, renewable diesel, and renewable naphtha during its initial ramp-up.
The U.S. EPA on July 8 hosted virtual public hearing to gather input on the agency’s recently released proposed rule to set 2026 and 2027 RFS RVOs. Members of the biofuel industry were among those to offer testimony during the event.
Upcoming Events










