Report: First ETBE made with US ethanol could reach Japan in 2019
SOURCE: USDA FAS GAIN
December 18, 2018
BY Erin Krueger
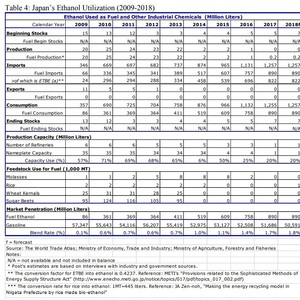
Japan is expected to import 890 million liters (235.11 million gallons) of fuel ethanol this year, mostly in the form of bio-ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE), according to an annual biofuels report the country recently filed with the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service’s Global Agricultural Information Network.
According to the report, the Japanese government extended its mandate to introduce 500 million liters (crude oil equivalent) of biofuels until 2022. Under the mandate, Japanese industry is expected to introduce 1.94 billion liters of ETBE into the market this year, which will contain 822 million liters of ethanol. Nearly all of that volume will be imported.
Advertisement
Advertisement
In April 2018, the country revised its policy to allow up to 44 percent U.S. corn-based ethanol in imported ETBE. Prior to that policy change, only Brazilian sugarcane ethanol was used. The report estimates the first shipment of ETBE containing U.S. ethanol could arrive in Japan in mid-2019.
According to the report, the national average blend rate for ethanol in Japan is only 1.8 percent. By 2022, the blend rate is expected to increase slightly to 1.9 percent.
Advertisement
Advertisement
The maximum ethanol blend rate in Japan is 3 percent due to concerns that higher ethanol blends could damage vehicles. The report indicates the country is not currently considering raising the blend rate limit beyond E3.
The report shows Japan currently has only one ethanol plant, with a nameplate capacity of 1 million liters. That facility operates at approximately 20 percent capacity. Capacity has dropped significantly since 2011, when the country had six ethanol plants with a combined nameplate capacity of 35 MMly. At that time, the facilities operated at near 70 percent capacity.
A full copy of the report is available on the USDA FAS GAIN website.
Related Stories
The U.S. Energy Information Administration maintained its forecast for 2025 and 2026 biodiesel, renewable diesel and sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) production in its latest Short-Term Energy Outlook, released July 8.
XCF Global Inc. on July 10 shared its strategic plan to invest close to $1 billion in developing a network of SAF production facilities, expanding its U.S. footprint, and advancing its international growth strategy.
U.S. fuel ethanol capacity fell slightly in April, while biodiesel and renewable diesel capacity held steady, according to data released by the U.S. EIA on June 30. Feedstock consumption was down when compared to the previous month.
XCF Global Inc. on July 8 provided a production update on its flagship New Rise Reno facility, underscoring that the plant has successfully produced SAF, renewable diesel, and renewable naphtha during its initial ramp-up.
The U.S. EPA on July 8 hosted virtual public hearing to gather input on the agency’s recently released proposed rule to set 2026 and 2027 RFS RVOs. Members of the biofuel industry were among those to offer testimony during the event.
Upcoming Events










